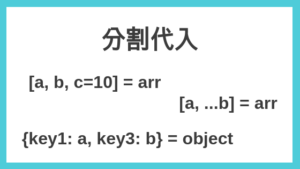
テスト対象の依存処理が未実装などの場合、テストを実行することができません。Sinon.jsを利用すると、テスト対象が依存している部分を置き換えてテストを実行することができます。
目次
インストール
mocha(テストフレームワーク) と chai(アサーションライブラリ) も合わせてインストールしておきます。
npm install sinon chai mochanpm run test でテストが実行できるように調整します。
{
(省略)
"scripts": {
"test": "mocha"
},
(省略)
}spy
( 入出力を記録, 実行後に検証, 置き換えない )
目的
spyは、以下の目的を持っています。
テスト対象からの「間接的な出力」を検証するために使う。出力を記録しておくことで、テストコードの実行後に、値を取り出して検証できる。
サンプル
const sinon = require('sinon')
const chai = require('chai')
const assert = chai.assert
class AnotherClass {
xyz(x) {
return x > 0
}
}
class TargetClass {
constructor(anotherClass) {
this.driver = anotherClass
}
targetMethod(x) {
const result = this.driver.xyz(x)
return result ? 100 : 0
}
}
describe('spy', () => {
it('targetMethod', () => {
// arrange
const anotherClass = new AnotherClass()
const targetClass = new TargetClass(anotherClass)
const spy = sinon.spy(anotherClass, 'xyz')
// act
targetClass.targetMethod(10)
targetClass.targetMethod(-5)
// assert
assert(spy.callCount === 2) // xyzが呼ばれた回数
assert(spy.getCall(0).args[0] === 10) // xyzが呼ばれた際の引数(1回目)
assert(spy.returnValues[0] === true) // xyzが呼ばれた際の戻り値(2回目)
assert(spy.getCall(1).args[0] === -5) // xyzが呼ばれた際の引数(1回目)
assert(spy.returnValues[1] === false) // xyzが呼ばれた際の戻り値(2回目)
})
})- spyを利用しても、spy対象のメソッドは実行されます。
- 実行後に、spy対象が実行された回数、引数や戻り値についてチェックします。
stub
( 依存処理を置き換える )
目的
stubは、以下の目的を持っています。
テスト対象に「間接的な入力」を提供するために使う。
サンプル
const sinon = require('sinon')
const chai = require('chai')
const assert = chai.assert
class AnotherClass {
xyz(x) {
// 未実装
}
}
class TargetClass {
constructor(anotherClass) {
this.driver = anotherClass
}
targetMethod(x) {
const result = this.driver.xyz(x)
return result ? 100 : 0
}
}
describe('stub', () => {
it('targetMethod', () => {
// arrange
const anotherClass = new AnotherClass()
const targetClass = new TargetClass(anotherClass)
const stub = sinon.stub(anotherClass, 'xyz')
stub.withArgs(10).returns(true)
stub.withArgs(-5).returns(false)
// act & assert
assert(targetClass.targetMethod(10) === 100)
assert(targetClass.targetMethod(-5) === 0)
stub.restore();
})
})- stubを利用すると、stub対象のメソッドは実行されません。
withArgsメソッドとreturnsメソッドで特定の引数が渡された時の戻り値を指定できます。restoreメソッドでstubでラップした状態を解除することができます。
mock
( 実行前に期待, 置き換える )
目的
mockは、以下の目的を持っています。
テスト対象からの「間接的な出力」を検証するために使う。テストコードの実行前に、あらかじめ期待する結果を設定しておく。検証はオブジェクト内部で行われる。
サンプル
const sinon = require('sinon')
const chai = require('chai')
const assert = chai.assert
class AnotherClass {
xyz(x) {
return x > 0
}
}
class TargetClass {
constructor(anotherClass) {
this.driver = anotherClass
}
targetMethod(x) {
const result = this.driver.xyz(x)
return result ? 100 : 0
}
}
describe('mock', () => {
it('targetMethod', () => {
// arrange
const anotherClass = new AnotherClass()
const targetClass = new TargetClass(anotherClass)
const mock = sinon.mock(anotherClass)
// act & assert
mock.expects('xyz').once().withArgs(10).returns(true)
assert(targetClass.targetMethod(10) === 100)
mock.expects('xyz').once().withArgs(-5).returns(false)
assert(targetClass.targetMethod(-5) === 0)
mock.restore()
})
})- mockを利用すると、mock対象のメソッドは実行されません。
- 実行前に期待する動作を設定します。
restoreメソッドでmockでラップした状態を解除することができます。